Machine Learning
Scaling of Neural Networks
The performance of artificial neural networks (ANNs) is getting better every year. A part of this improvement is because of better architectures, but the other part is because neural networks and their training data are getting bigger. I, along with several colleagues at Johns Hopkins and Google, have been working to figure out the mathematical models that govern the scaling of ANN performance with their size and with the size of training data. We have also tested our theories using experiments on well known datasets.
- Related Publications:
- arxiv: 2004.10802
- arxiv: 2102.06701
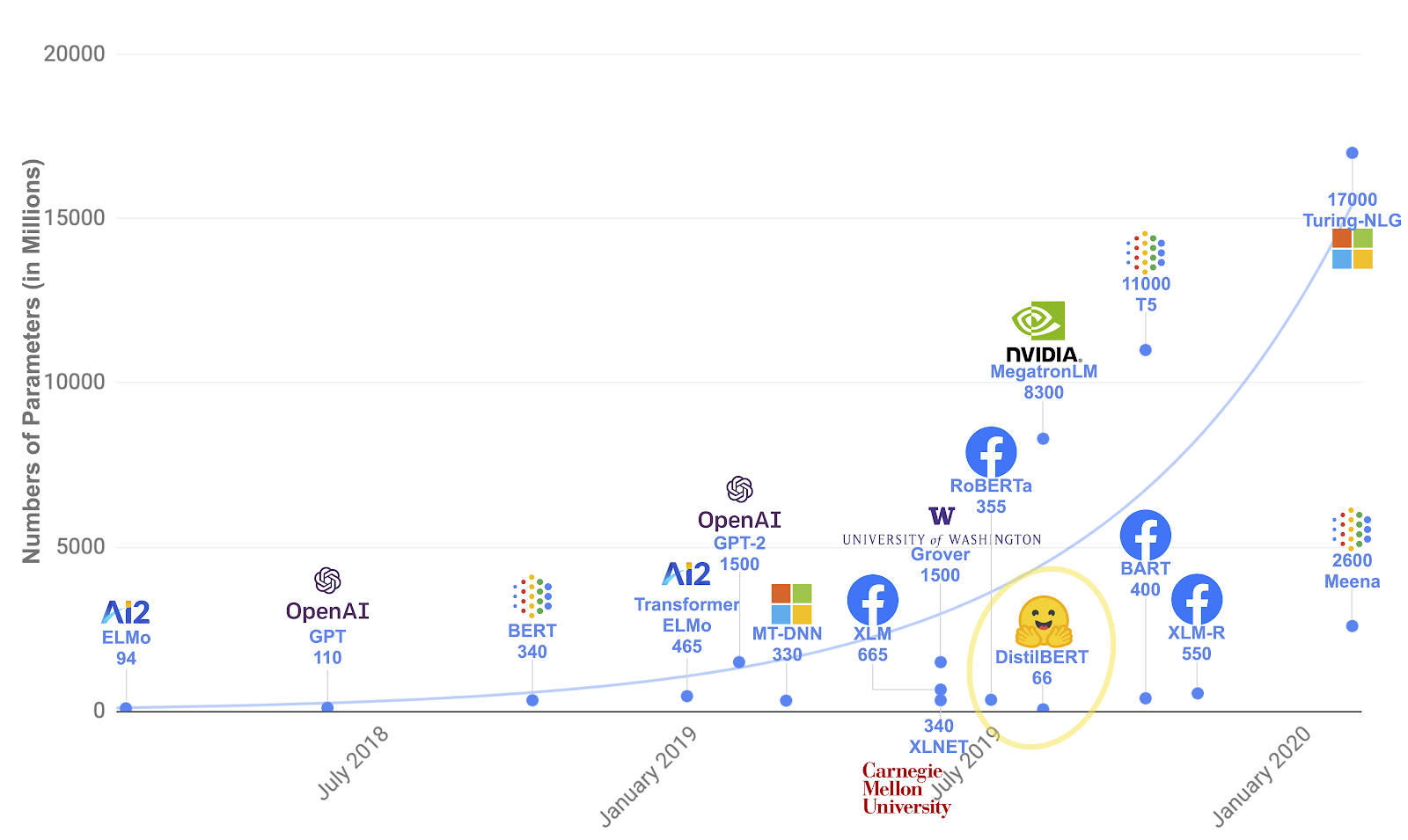
The sizes of major AI models are increasing very rapidly. Source: AI Multiple
Optimization with Birthoff Polytopes
Machine learning problems, including neural networks, are usually non-convex optimizations. In general, non-convex optimizations are mathematically untractable. Convex optimizations, on the other hand, can be studied in a variety of cases. As an undergraduate, I worked on convex optimization problems involving Birkhoff polytopes. The reason being that Birkhoff polytopes show up in a wide variety of optimization problems.
- Related Unpublished Work:
- undergraduate thesis
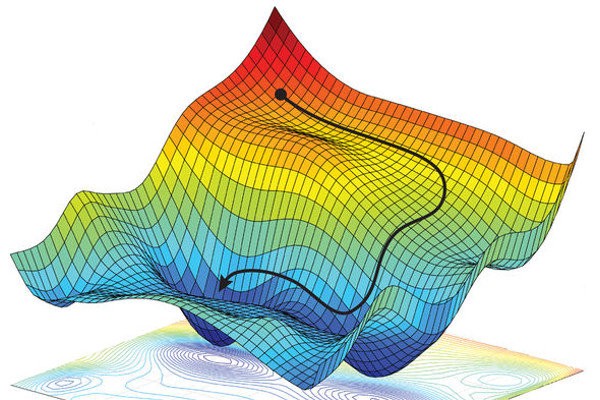
Machine learning problems are usually non-convex, as shown above schematically. Convex optimization is the simpler version that can be handled with mathematical rigor to some extent. Source: medium
Theoretical Physics
Reconstructing Quantum Gravity from CFT
Quantum mechanics is incompatible with Einstein's general theory of relativity. This problem has been unsolved since the 2nd half of the 20th century. The aim is to find a unified theory of quantum gravity that explains all phenomena of nature under one roof. String theory seemed to be a promising contender for a while, but it was soon realized that we need to look elsewhere (see Peter Woit's blog). Consequently, a property called holography was discovered which linked quantum gravity to a pure quantum theory in a specific mathematical construction. We use holography to construct the properties of quantum gravity from ground up. In particular, we have developed tools that can probe the unique non-locality property of quantum gravity.
- Related Publications:
- arxiv: 1905.00015
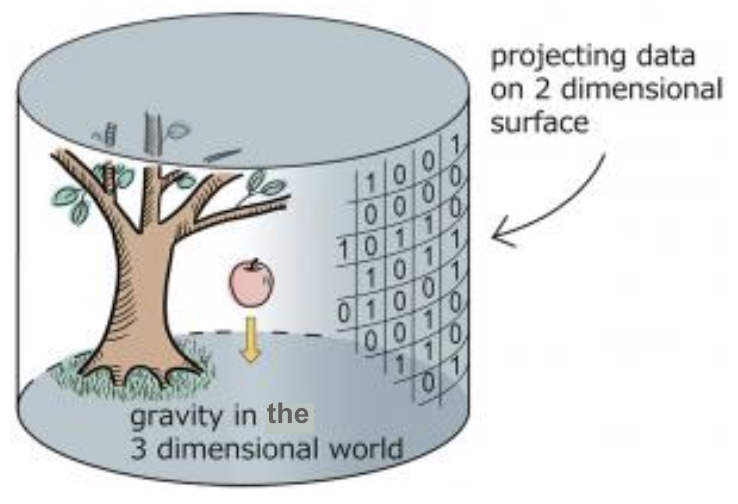
Hologrpahy is the principle that quantum gravity in the bulk spacetime is related to a special quantum theory on the boundary (a 'CFT')
Dyanamics of Black Holes
The dynamics of black holes is governed by Einstein's general theory of relativity (GR). GR is a mathematically complex theory, with few exact solutions. As an undergraduate, I worked on developing a formalism that gives us an analytical handle on black hole dynamics.
- Related Publications:
- arxiv: 1611.09310
Sanskrit, Linguistics and NLP
Paninian Algorithm of Sanskrit
When we think of natural languages (i.e. human languages), we usually imagine a messy, at times arbitrary, set of rules that are hard to pin down completely. Sanskrit is quite the opposite of that. In about 4000 rules, Panini (IAST: Pāṇini देव: पाणिनि) completely characterized the language around 2400 BC. I'm in the process of studying this seminal work called Aṣṭādhyāyī. The work also contains various insights into linguistics. Pāṇini's algorithmic approach has applications in computer science, for example in the field of natural language processing (NLP).
An Indian postal stamp to commemorate Pāṇini. The saying goes that Pāṇini "captured the ocean in a cow's hoofprint".